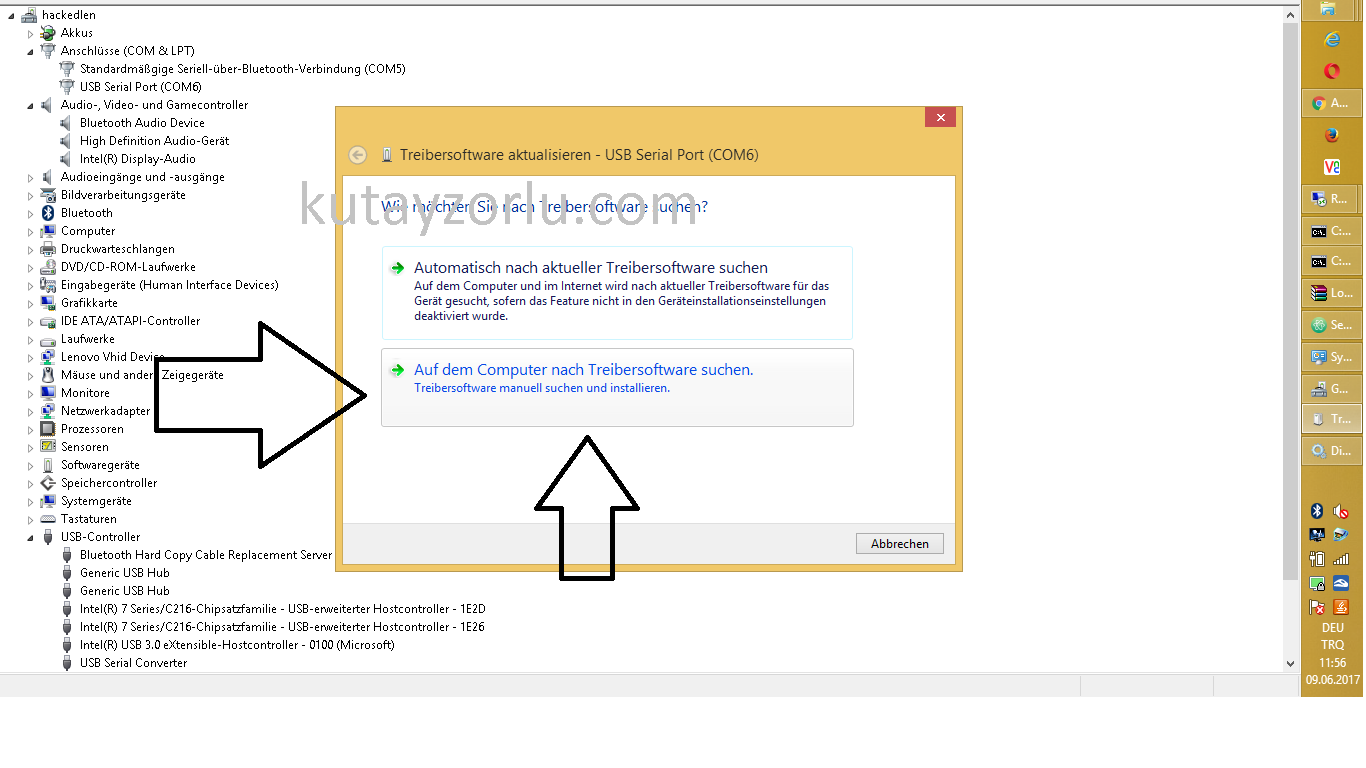
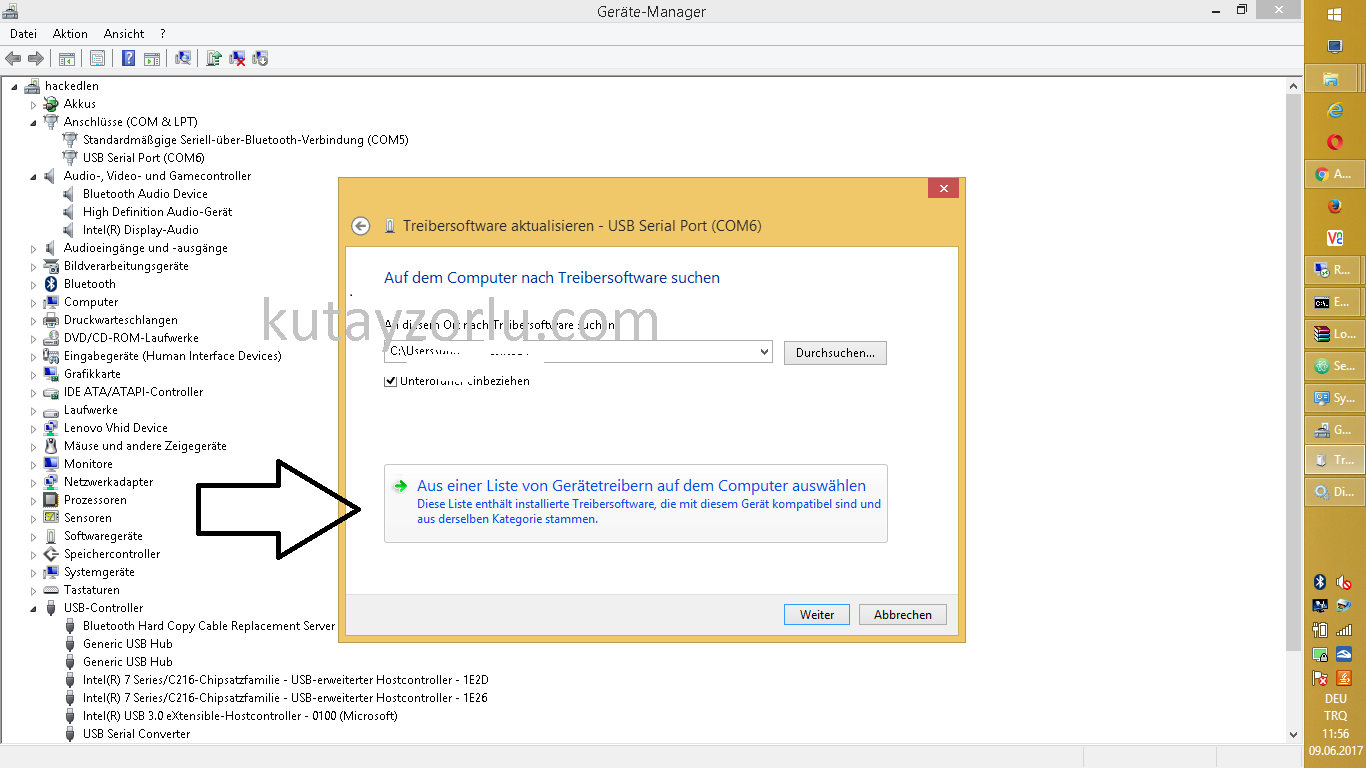
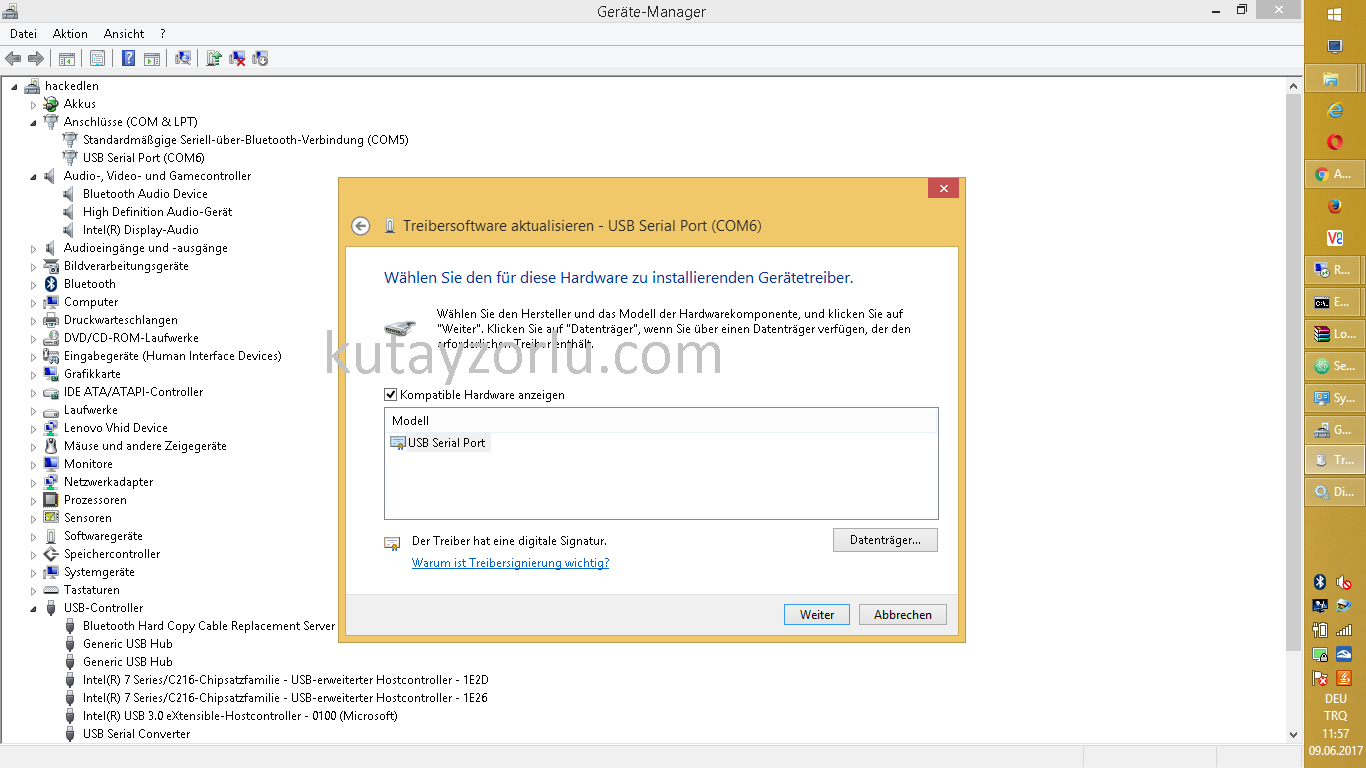
Listen on interface eth0:
Listen on any available interface :
Be verbose while capturing packets:
More verbose while capturing packets:
Very verbose while capturing packets:
Verbose and print the data of each packet in both hex and ASCII, excluding the link level header:
Verbose and print the data of each packet in both hex and ASCII, also including the link level header:
Less verbose (than the default) while capturing packets:
Limit the capture to 100 packets:
Record the packet capture to a file called capture.cap:
Record the packet capture to a file called capture.cap but display on-screen how many packets have been captured in real-time:
|
|
tcpdump -v -w capture.cap |
Display the packets of a file called capture.cap:
Display the packets using maximum detail of a file called capture.cap:
|
|
tcpdump -vvv -r capture.cap |
Display IP addresses and port numbers instead of domain and service names when capturing packets
Capture any packets where the destination host is 192.168.5.1. Display IP addresses and port numbers:
|
|
tcpdump -n dst host 192.168.5.1 |
Capture any packets where the source host is 192.168.5.1. Display IP addresses and port numbers:
|
|
tcpdump -n src host 192.168.5.1 |
Capture any packets where the source or destination host is 192.168.5.1. Display IP addresses and port numbers:
|
|
tcpdump -n host 192.168.5.1 |
Capture any packets where the destination network is 192.168.5.0/24. Display IP addresses and port numbers:
|
|
tcpdump -n dst net 192.168.5.0/24 |
Capture any packets where the source network is 192.168.1.0/24. Display IP addresses and port numbers:
|
|
tcpdump -n src net 192.168.5.0/24 |
Capture any packets where the source or destination network is 192.168.5.0/24. Display IP addresses and port numbers:
|
|
tcpdump -n net 192.168.5.0/24 |
Capture any packets where the destination port is 23. Display IP addresses and port numbers:
Capture any packets where the destination port is is between 1 and 1023 inclusive. Display IP addresses and port numbers:
|
|
tcpdump -n dst portrange 1-1023 |
Capture only TCP packets where the destination port is is between 1 and 1023 inclusive. Display IP addresses and port numbers:
|
|
tcpdump -n tcp dst portrange 1-1023 |
Capture only UDP packets where the destination port is is between 1 and 1023 inclusive. Display IP addresses and port numbers:
|
|
tcpdump -n udp dst portrange 1-1023 |
Capture any packets with destination IP 192.168.1.1 and destination port 23. Display IP addresses and port numbers:
|
|
tcpdump -n "dst host 192.168.5.1 and dst port 23" |
Capture any packets with destination IP 192.168.5.1 and destination port 80 or 443. Display IP addresses and port numbers:
|
|
tcpdump -n "dst host 192.168.5.1 and (dst port 80 or dst port 443)" |
Capture any ICMP packets:
Capture any ARP packets:
Capture either ICMP or ARP packets:
Capture any packets that are broadcast or multicast:
|
|
tcpdump -n "broadcast or multicast" |
Capture 500 bytes of data for each packet rather than the default of 68 bytes:
Capture all bytes of data within the packet: